Neuromonitoring, also known as intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM), is a medical technique that surgeons use during surgeries to assess and protect the nervous systems of the patients. This is done to ensure the functional integrity of the neural structures including brain and nerves. The technique uses different electrophysiological methods to make this real-time assessment of the patient’s nervous system.
This blog describes all about neuromonitoring and how it helps patients and surgeons in successfully completing complex surgical procedures.
What Is Neuromonitoring?
Neuromonitoring can be known by different names, such as surgical monitoring, intraoperative neuromonitoring or intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring, or nerve monitoring. In this process, a surgical neurophysiologist applies electric currents on the patients’ brain and then a physician continuously monitors and interprets the waveforms.
Surgical neurophysiologist uses this procedure for patients which are at a risk of neural injury. Based on his feedback, surgeons performing brain surgery can make better medical decisions.
The intraoperative neuromonitoring can be used in different surgical cases such as during spinal trauma, enlarged thyroids, spinal curvature, tethered cords, tumors, implanting spinal cord stimulators or while removing plaque from arteries.
Techniques And Technologies Used In Intraoperative Neuromonitoring
Intraoperative neuromonitoring uses different methods to assess a patient’s condition. However, the choice of methods depends on the surgery type and the neural structures which are at risk. Collectively, different techniques in intraoperative neuromonitoring ensure patients safety and improve his condition during critical circumstances.
Here are some techniques and technologies that surgical neurophysiologist use during intraoperative neuromonitoring:
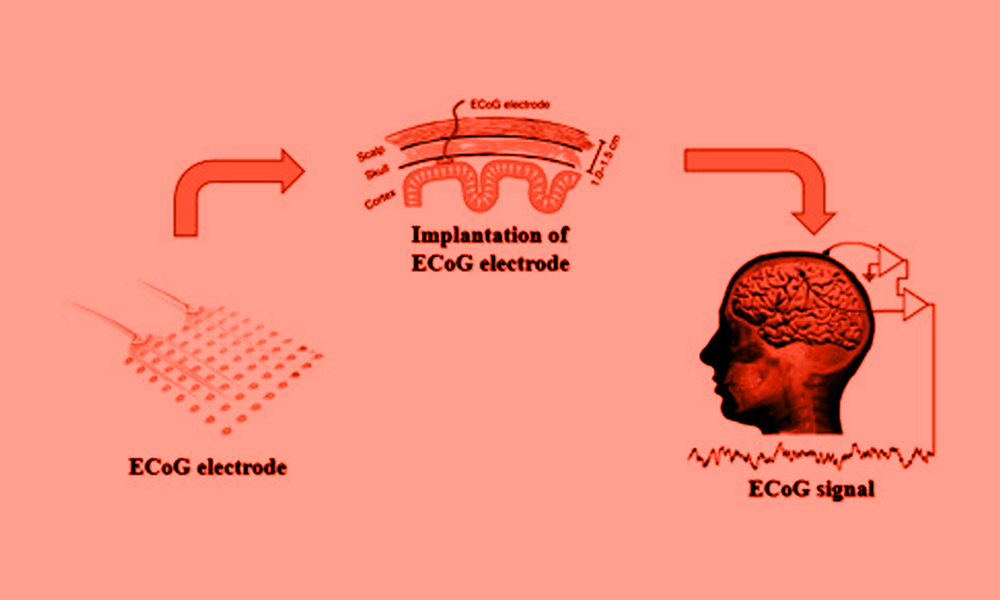
- Electrocorticography: Abbreviated as ECoG, this method records brain activity of the patients from the cortical surface. Surgeons may use this procedure during brain tumor resections or in epilepsy surgeries.
- Electroencephalography: In this method, brain activity is recorded by placing electrodes on the scalp. With this, surgeons can monitor brain activity, assess anesthesia depth and detect any potential risk of seizures. It can also predict cognitive dysfunction after surgery. Based on the amplitude size and frequency during brain activity, surgeons can recover adequate blood flow to the brain.
- Electromyography: Abbreviated as EMG, this intraoperative neuromonitoring method measures electrical activity of the muscles during surgery. Basically, it monitors nerve functioning during spine surgery, facial nerves during facial surgeries, and other nerves functioning during other types of surgical procedures. These include removal of tumor, thyroidectomy or in brachial plexopathy exploration.
- Somatosensory Evoked Potentials: Abbreviated as SSEPs, this technique stimulates peripheral nerves to evaluate sensory pathways and also record brain responses. During surgeries, SSEPs help assess spinal cord functioning and detect any potential damage.
- Motor Evoked Potentials: Abbreviated as MEPs, this technique stimulates the motor cortex to evaluate motor pathways and record muscle responses. With this intraoperative neuromonitoring technique, surgeons can monitor the spinal cord and the functioning of motor nerves.
- Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potentials: Abbreviated as BAEPs, this technique stimulates brainstem responses through sound and evaluates auditory pathways.
- Intracranial Pressure Monitoring: Also known as ICP, this is an invasive intraoperative neuromonitoring technique. In this, surgeons place a sensor or catheter in the patient’s skull to assess changes in pressure. High pressure changes detected during this method helps surgeons act immediately to prevent brain swelling.
- Cerebral Perfusion Pressure: Also known as CPP, this method evaluates blood flow to the brain and guides treatment accordingly.
- Visual Evoked Potential: In this intraoperative neuromonitoring technique, surgeons monitor the functionality of the optic nerves and optic pathways. It helps prevent and minimize visual impairments during the intraoperative period.
What Is The Importance Of Intraoperative Neuromonitoring In Clinical Practice?
Undoubtedly, it plays a critical role in medical practices. With the different techniques mentioned above, surgeons can manage patients’ condition during complex brain surgeries or in surgeries that affect the nervous system. Here are some key points that highlights its importance:
Early Detection Of Neurological Complications With Neuromonitoring
Neuromonitoring helps early detection of any potential neurological damage or injury during treatment so that surgeons can act accordingly. Timely detection of any secondary cerebral insults or deteriorating neurological condition helps prevent any irreversible damage to the brain and nervous system.
Guiding Treatment Decisions Through Neuromonitoring Data
Based on the physiological data provided by different methods, it guides the physiologists and surgeons to individualize therapy and also improves the understanding of diseases during critical illness.
Prognostication
Neurological data obtained in intraoperative neuromonitoring helps in prognostication so that clinicians can predict any possible outcomes.
Ensuring Patients Safety Through Intraoperative Neuromonitoring
The data obtained during intraoperative neuromonitoring helps prevent any permanent damage to the patients’ nervous system by alerting your healthcare provider of any potential injury.
Providing Customized Care
Based on several invasive and non-invasive tools, healthcare professionals can precisely get to know about patients’ condition and customize their treatment based on the data available.
Future Directions and Advancements In Intraoperative Neuromonitoring Technology
It has deep potential to grow more effective and comprehensive in times to come. Coupled with other conventional neural monitoring techniques such as EMG, EEG etc., intraoperative neuromonitoring technology can render better injury predictions. Increasing digital signal processing speeds and new data acquisition techniques will improve consistency in IONM results.
At the same time, sensitivity in data acquisition can be enhanced to capture even the slightest change in neural response. At underdeveloped locations, Intraoperative neuromonitoring technology can prove to be a major lifesaver. Intraoperative neuromonitoring technology can further be advanced into a non-invasive real time monitoring technique in future. Such a non-invasive real time monitoring form of IONM can help to a great extent in post operative patient care as well. Such advancements can prove IONM as an inseparable part of safe neurological surgeries in future.

Intraoperative neuromonitor is deficiently an attractive option for monitoring patients’ nervous systems but it is essential to invest in appropriate tools and measures that can facilitate correct neuromonitoring. At Biosys Biomedical, you get a comprehensive range of neuromonitoring solutions. We also offer fast and on-site service along with personal contacts so that you can have the reliable support you wish for.
We provide you easy to use devices so that users can easily interpret the signals and also identify critical signal changes instantly. Contact us with your requirements and we will suggest the best possible solution with us.
References
Intraoperative Neuromonitoring – The Complete Guide… – Intraoperative Neuromonitoring
untitled (wfsahq.org)
The Importance of Neuromonitoring in Non Brain Injured Patients | Critical Care | Full Text (biomedcentral.com)
Clinical review: Neuromonitoring – an update | Critical Care | Full Text (biomedcentral.com)

